Nested Marquee tag in HTML It is used to insert scrolling image or text. In simpler terms it can be understood that it scrolls text or images in various directions like left, up, or right. It does this automatically.
The text that is included in the marquee tag scrolls from left to right. The marquee tag within HTML is no longer supported in HTML5 however we are able to utilize it in earlier version of HTML and shouldn’t be used in any further ways.
It is recommended that you make use of CSS instead to create the same effect of scrolling.
What is Nesting?
Nesting allows for powerful, yet simple programming. It reduces the amount of code needed, while making it simple for a programmer to debug and edit.
It is quite commonplace when it comes to programming where various logic structures such as are combined. Sequence, selection and loop are combined.
Most of people confused what is nested ? but this is so simple such as loop which repeats it self till the prescribed value and in the loop there can be empty space or any written programming code or HTML code to execute it repeatedly.
Lets play with Marquee
<!doctype html>
<html>
<head>
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<marquee direction="down" height="500px" behavior="alternate">
<marquee scrollamount="20" direction="right" > <img src="giphy.gif" > </marquee>
</marquee>
</body>
</html>Output
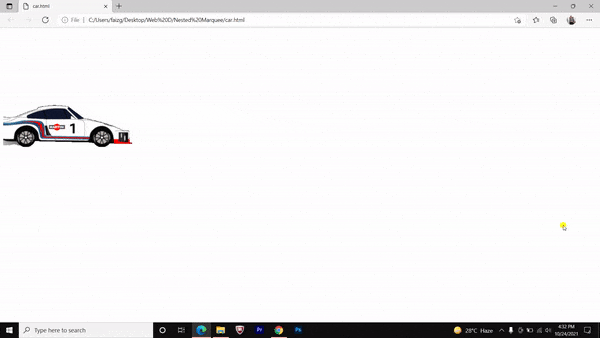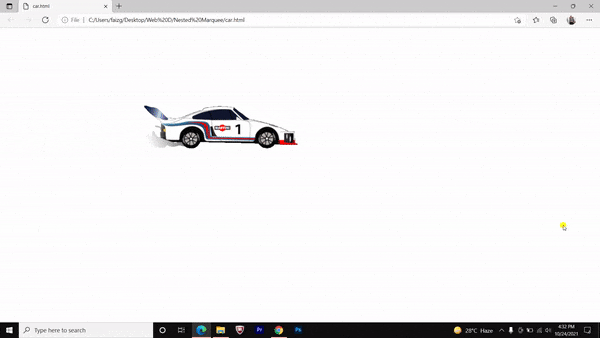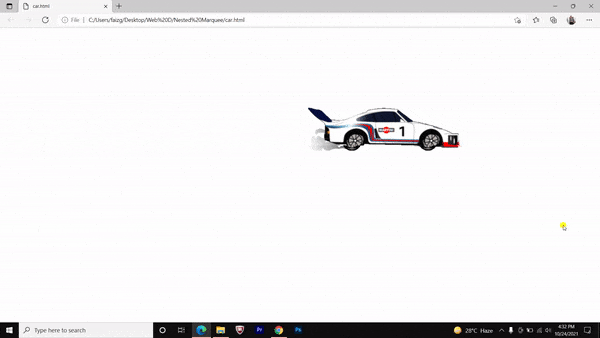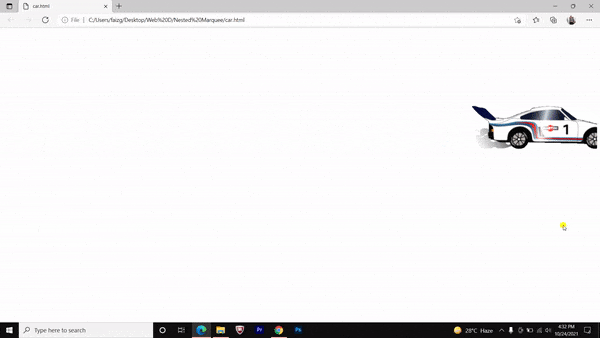
Nested marquee tag Pros and Cons
Advantage
- They immediately draw attention to themselves
- And perhaps most of all: they are relatively rare meaning that they’ll be memorable and all the more likely to stand out
- They are fun and quirky
- The layout and design is perfectly suited to entertaining
Disadvantage
- Marquee may be distracting because human eyes are attracted towards movement and marquee text constantly.
- Since Marquee text moves, so it is more difficult to click static text, depending on the scrolling speed.
- It is a non-standard HTML element.
- It draws user’s attention needlessly and makes the text harder to read.
Conclusion
We have made a running car by nesting the marquee tag and it’s attributes. You can do it further with a bouncing ball and flying birds etc.
Note
Watch Nested Marquee tag on YouTube – Click here
Learn Marquee tag in HTML & it’s all hidden attributes – Click here
Watch Marquee tag in HTML on YouTube – Click here
Password – technobrainz

